What is oxidation reaction?
(1) Broadly speaking, the chemical transformation process in which the oxidation number of carbon atoms in organic molecules increases is called oxidation reaction.
(2) in a narrow sense, it refers to the reaction of increasing oxygen and losing hydrogen in organic molecules.
③ Olefins, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, active methylene compounds and aromatic hydrocarbons can be converted into corresponding alcohols, epoxides, aldehydes, ketones and acids by oxidation reaction.
There are many kinds of oxidation reactions, and the common points shown include:
① There are many kinds of oxidants, the same oxidant can complete the oxidation of different substrates, and the same substrate can be oxidized by different oxidants, and the oxidation products strongly depend on the reaction conditions.
(2) The oxidation reaction is a strong exothermic reaction, and the heat is removed in time, so that the reaction proceeds smoothly.
③ Oxidation reaction can be regarded as irreversible reaction in thermodynamics, especially complete oxidation reaction.
④ There are many side reactions in the oxidation process.
There are many kinds of oxidants, and their action characteristics are different:
(1) One oxidant can oxidize a variety of different groups, and the same group can give different oxidation products due to different oxidants and reaction conditions.
② The oxidant which is cheap and widely used in industry is air or oxygen. Oxidants other than air and oxygen are always called chemical oxidants; The reactions using chemical oxidants are collectively referred to as "chemical oxidation".
③ Chemical oxidants are generally expensive and pollute the environment. Developing cheap, low-pollution and high-efficiency chemical oxidants is an eternal research topic for pharmaceutical chemistry researchers.
N- methylmorpholine manufacturers introduce common oxidant types:
(1) high-priced compounds of metal elements. E.g., KMnO4, MnO2, cro3, k2cr2o7, PBO2, TL (NO3) 3, ce (NO3) 4, etc.
② High valence compounds of nonmetallic elements. Such as HNO3, N2O4, SO3, naclo, naclo3, naio4, DMSO, etc.
③ Inorganic oxygen-enriched compounds. Such as ozone, hydrogen peroxide, sodium peroxide, sodium percarbonate and sodium perborate.
④ Organic oxygen-enriched compounds. E.g., organic peroxides, including CH 3 CO 3 H, t-BuOOH, etc.
⑤ Non-metallic elements. Such as halogen, etc.
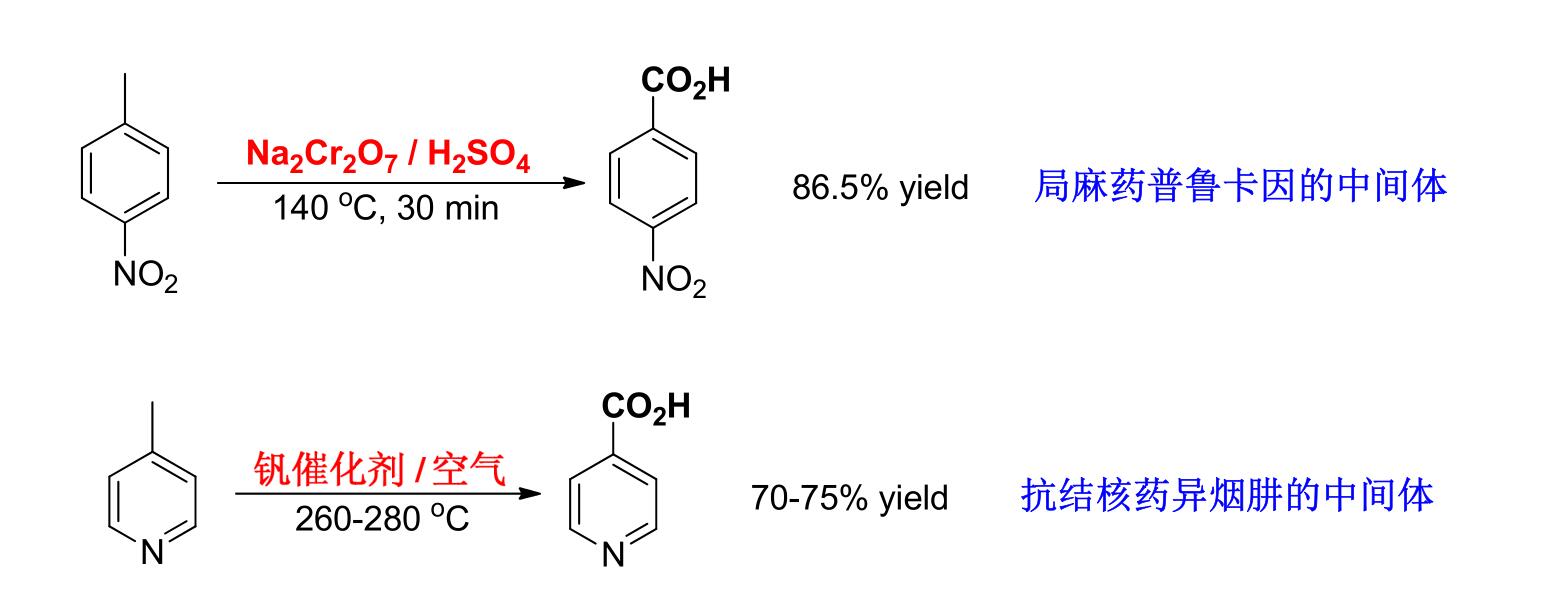
I. Liquid phase catalytic oxidation
① Commonly used catalysts are transition metal ions such as cobalt salt, manganese salt, copper salt, platinum-carbon and chromium oxide.
② In liquid-phase catalytic oxidation, air or oxygen is mainly consumed, and the reaction is generally carried out at 100-200℃ and under low pressure.
③ p-nitroacetophenone is an important intermediate for the synthesis of chloramphenicol, which is prepared from p-nitroethylbenzene by liquid-phase air oxidation.
④ Liquid-phase catalytic oxidation is a radical reaction. For reactions with a particularly long induction period, it is often necessary to add a small amount of promoters in addition to catalysts.
⑤ There are two kinds of accelerators: a) organic oxygen-containing compounds, such as acetaldehyde, ether or butanone; B) bromides such as ammonium bromide, ethane bromide, carbon tetrabromide, etc.
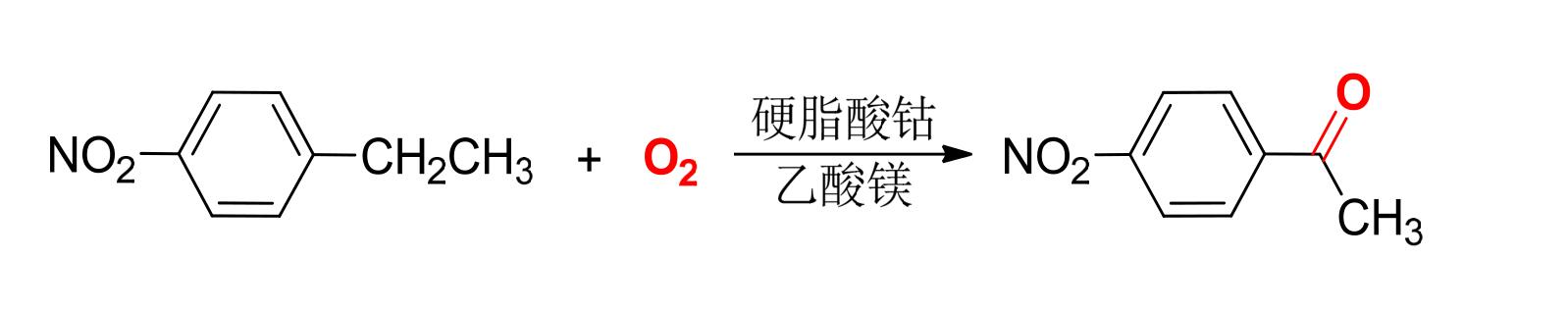
Second, the gas phase catalytic oxidation
(1) Gas-phase catalytic oxidation is mostly used for the oxidation of easily gasified compounds, which requires that raw materials and products have sufficient thermal stability and are not easy to be decomposed or deeply oxidized.
② common catalysts include metals and metal oxides. metal catalysts include Cu, Co, Ag, Pt,Pd and PD, while metal oxide catalysts include V2O5, MoO3, bi2o3, Fe2O3, sb2o3, seo2, teo2 and Cu 2 O.
③ In practice, most of them are multi-component composites, which can also be loaded on silica gel, zeolite, molecular sieve and other materials. V 2 O 5 is the most commonly used oxidation catalyst.
④ The reaction is usually carried out in a tubular fixed bed or fluidized bed.
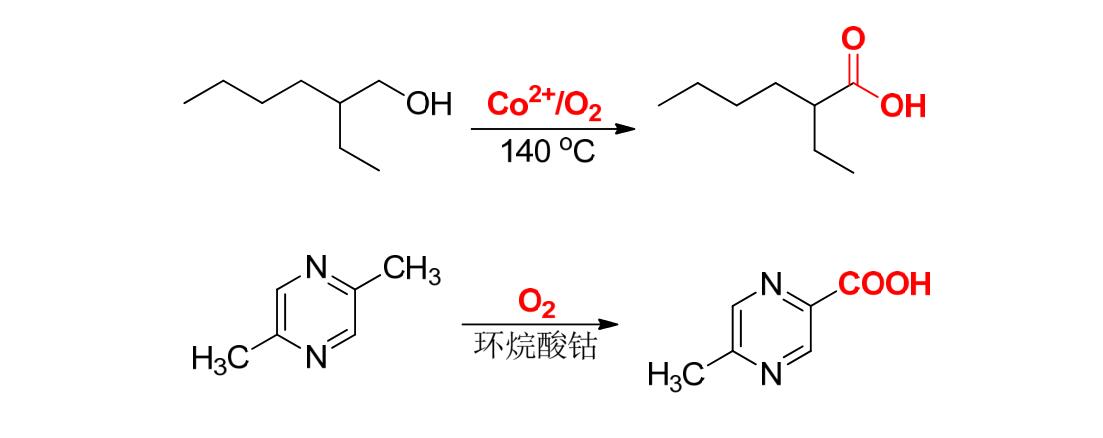
⑤ Using bivalent cobalt salt as catalyst, primary alcohol is oxidized into carboxylic acid by air.
⑥5- methylpyrazine -2- carboxylic acid is an intermediate in the synthesis of glipizide, which can be prepared from 2,5- dimethylpyrazine by catalytic oxidation.
⑦ Air oxidation is a free radical reaction, which produces hydroperoxide, which is decomposed into corresponding oxidation products.
⑧ Single-state O 2 can form cyclic peroxides with some compounds with diene structure or similar diene structure under the action of light, microwave or hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, alkyl hydrogen peroxide, peroxy acid and other oxidants at low temperature or room temperature.
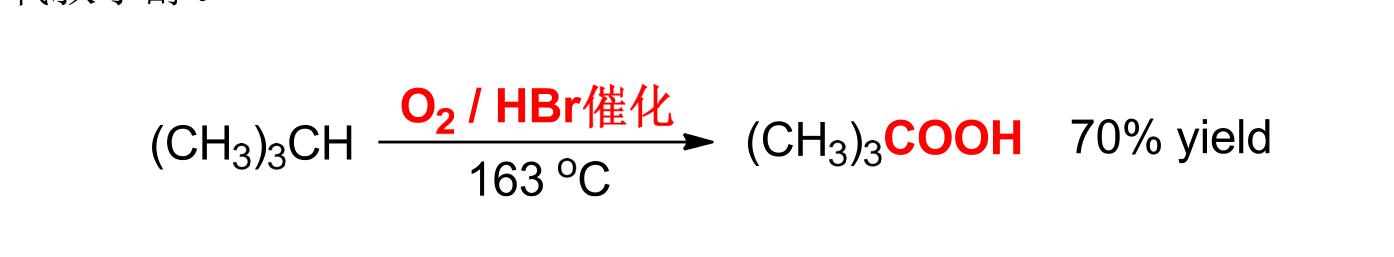
⑨ Selective oxidation of C-H bond in saturated hydrocarbon molecule is quite difficult, but for tert-butane with special structural form, it can be oxidized into peroxide under the action of HBr with catalyst amount
Oxytert-butanol.
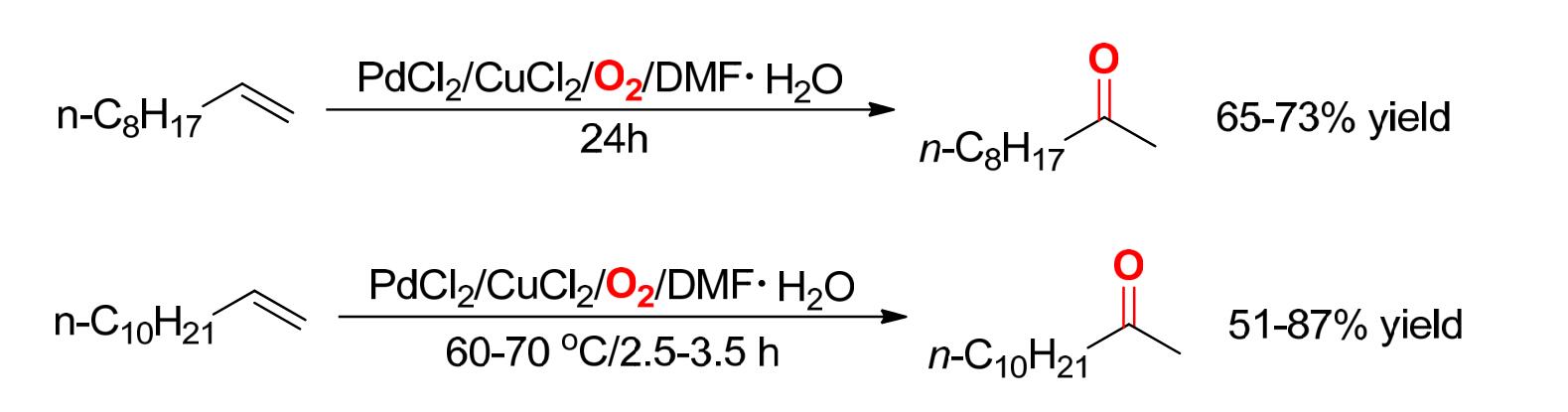
⑩Wacker 反应:在PdCl 2 /CuCl 2 存在下,利用空气中的 氧气使烯烃转化为醛或酮的反应。
3. High-valent ruthenium is used as oxidant
① ruthenium tetroxide (RuO 4) is a mild oxidant, which can oxidize secondary alcohol into ketone with water as solvent or inert solvent under mild conditions. During oxidation, RuO 4 is often used in combination with sodium periodate or sodium hypochlorite, and is added with alcohol in the same amount.
② Alcohols with hydroxy lactone structure unstable to acid or base and cyclobutanol compounds with high tension can also be oxidized into corresponding ketones with high yield by RuO 4.
③ Ruo _ 4 is also effective in the oxidation of sugar hydroxyl groups, and Ruo _ 4 does not destroy some protected hydroxyl groups on sugar.

④R(RuO 4)-type salts (R = Pr 4 N, Bu 4 N, PPh 4, N(PPh 3) 4) can be used in combination with oxidants to oxidize alcohol under milder reaction conditions. Among them, TPAP (tetra-n-propyl ammonium perruthenate) is a typical representative.
⑤ N- methylmorpholine oxide (NMO) was used as co-oxidant, TPAP was added at low temperature or room temperature, and the reaction was completed by stirring with alcohol for 5min to 1 h.
⑥TPAP has obvious selectivity and universality. When there are both primary and secondary hydroxyl groups in the molecule, the oxidation rate of primary hydroxyl groups is relatively fast. However, TPAP is still a very effective oxidant for secondary alcohols, even hemiacetal.